Patent Quality Index
(PQI)
OECD's PQI > Introduction to Patent Quality Index (PQI)
Introduction to OECD’s PQI
-
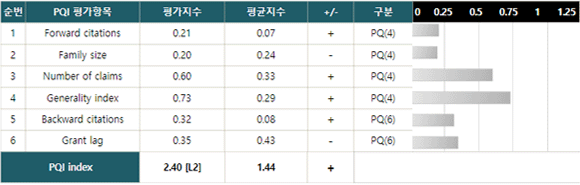
- Patent Quality Index (PQI), as proposed by OECD, measures the technological and commercial values of technological innovation using patent information, with six sub-indexes including forward citation, family size, the number of claims, generality index, backward citation and grant lag.
- It was designed based on documentation by Mariagrazia Squicciarini, Hélène Dernis and Chiara Criscuolo (OECD), “MEASURING PATENT QUALITY: INDICATORS OF TECHNOLOGICAL AND ECONOMIC VALUE”, DSTI/DOC (2013).
-
Patent quality (PQ) synthesises economic and technological value of patents.
Accounts for 4 to 6 dimensions:
- PQ(4): Forward citations; family size; number of claims; generality index.
- PQ(6) = PQ(4) + Backward citations; grant lag. -
Definition (based on Lanjouw & Shankerman, 2004):
Unweighted average of normalised 4 (or 6) components. Patents cohorts stratified by year & tech field.
Higher quality => more valuable patent. - A complete PQI using all 6 sub-indexes can be calculated for U.S. patents by using forward citations, but as forward citations are unavailable for Korean and Japanese patents, PQI is calculated using the three sub-indexes instead: number of claims, family size, and grant lag.
- U.S. patents use all of PQ(6) indexes and arrive at the same score as OECD’s PQI Index.
- The higher the index, the higher the quality level.
- Each sub-index has the same weighted value of 1, with a minimum of 0 and a maximum of 1.
- An absolute score may be used, and stanine scores can be applied to the given grades according to their registered year and scores for each technical field.
- The detailed categories of the Patent Quality Index (PQI) are as follows.
-
평가항목 세부지표명(영문) 세부지표명(국문) 의미 산출방법 Forward citations 피인용지수 It shows the number of references used by a patent applied later than a target patent and generally indicates technology’s influence, similar in concept to “Impact Factor” of a thesis. The better the quality of the patent, the higher the number of references. After removing the upper 1 % and the lower 1% of data values, the number of family patents, the number of forward citations, the number of claims by technology classification, and a registration year,
it divides the number of claims, the number of forward citations and the number of family patents by a registration year and the maximum of technology classification. respectively, to normalize it to a value of 0 ~ 1Family size 패밀리 특허지수 It shows the number of countries in which patent applications of the same invention have been applied due to a target patent and a priority claim. The better the quality of patent, the more family size it has. Number of claims 청구항지수 It indicates the number of claims and the patent protection coverage for technology. The better the quality of patent, the higher the number of claims it has. Generality index 범용성 지수 It indicates the number of technical fields which have an influence on technology and technology diffusion in other fields By utilizing IPC of a patent referring to an individual patent, the patent which has a large number of IPCs is considered to be a wide use for technology.
i.e. the number of IPCs is 1, it is 0 and as the number of IPCs is increasing, it is getting close to 1.Backward citation 인용지수 It shows a patent reference used before a target patent is applied. The better the quality of patent, the higher the number of preceding patent references. After removing the upper 1% and the lower 1% of a registration year and the number of the references by technology classification,
It divides the number of references of an individual patent by the registration year and the maximum of technology classification, to normalize it to a value of 0 ~ 1.Grant lag 특허등록소요기간 It means the period of time after which a patent has been applied for and registered. The better the quality of patent, the earlier the patent is registered. After removing the upper 1% and the lower 1% of the registration year and the duration of registration,
: 1 – it means (registration lead time/ the maximum value of the duration of registration).PQI index 특허품질지수 It is a method of calculation of a patent quality index which sums up each normalized index without a weighted value, developed by OECD. Each index is fully qualified, having a weight value of 1
Korea/Japan : (Family size+Grant lag+Number of claims)/3
The United States: (Family size+Grant lag+Number of claims+Backward citation +Grant lag)/6 -